
Understanding ASC 842: How Real Estate Firms Can Ensure Compliance Without Complexity
- January 9, 2026
- Davinder Singh

If you run a real estate firm or manage properties, you’ve likely heard about ASC 842. But what exactly is it, and why should you care? ASC 842 is the new lease accounting standard issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) that fundamentally changed how companies report leases on their financial statements. Simply put, this standard requires most leases to appear on your balance sheet—something that wasn’t required before.
For real estate firms, this shift is particularly significant. Whether you’re a landlord, property manager, or tenant, ASC 842 affects how your leases are recorded, reported, and analyzed. The good news? Understanding it doesn’t have to be complicated. This guide will break down ASC 842 into simple, actionable steps so you can ensure compliance without the headache.
Key Point: ASC 842 became effective for public companies in January 2019 and for private companies in January 2022. If you’re not already compliant, now is the time to act.

Let’s start with the basics. ASC 842 replaced the older ASC 840 standard to bring greater transparency to lease obligations. The core idea is straightforward: companies must now show most of their leases on their balance sheet.
Under the old system (ASC 840), operating leases could stay off the balance sheet entirely. This meant that a company’s true financial obligations weren’t fully visible to investors, lenders, and other stakeholders. ASC 842 changed that by requiring both operating and finance leases to be recognized on the balance sheet.
When a lease commences, your company must:
For real estate firms, this means the square footage you lease, the parking spaces you rent, or any other property usage rights must now appear as assets and liabilities on your balance sheet.
The shift to ASC 842 has three major implications:
Understanding the differences between the old and new standards helps explain why compliance matters so much.
| Aspect | ASC 840 (Old Standard) | ASC 842 (New Standard) |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Leases | Off-balance sheet | On-balance sheet |
| Balance Sheet Recognition | Only capital leases recognized | All leases (operating and finance) recognized |
| ROU Asset | Not required | Required for all leases |
| Lease Liability | Only for capital leases | Required for all leases |
| Income Statement Treatment | Single rent expense | Split into depreciation and interest |
| Transparency | Lower visibility of obligations | Full visibility of all lease commitments |
| User of Discount Rate | Interest rate implicit in lease | Interest rate implicit in lease, or Incremental Borrowing Rate (IBR) if not available |
Why This Matters: The shift from off-balance sheet to on-balance sheet accounting means your liabilities increase, which can affect your credit ratios and financial metrics used by lenders and investors.
One of the most critical aspects of ASC 842 is correctly classifying your leases. A lease is either operating or finance, and the classification determines how you account for it.
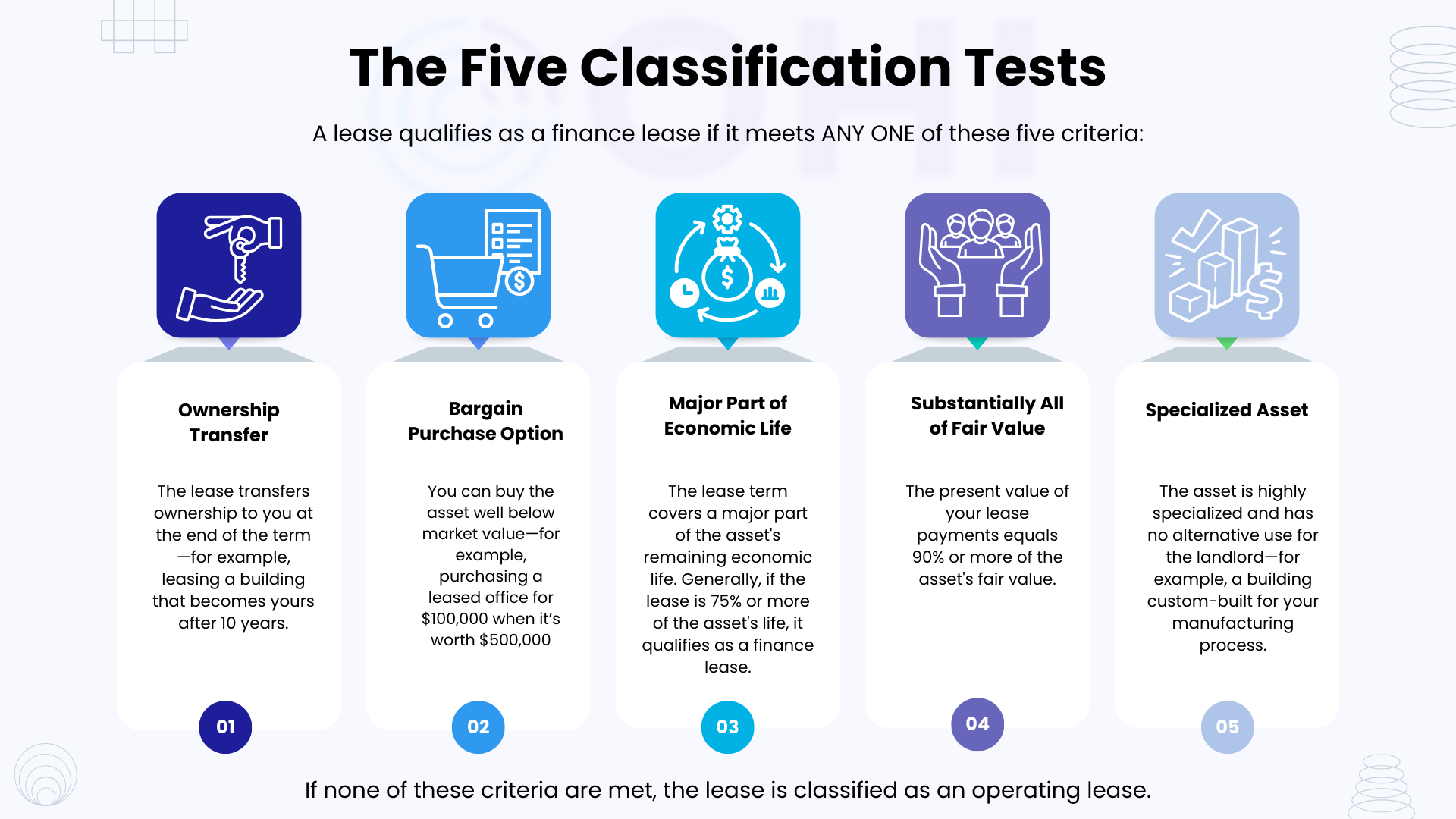
| Classification | Balance Sheet Impact | Income Statement Impact | Financial Ratio Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Lease | ROU asset and lease liability recognized | Straight-line expense recognized | Lower immediate expense recognition |
| Finance Lease | ROU asset and lease liability recognized | Front-loaded expense (depreciation + interest) | Higher initial expenses, lower later expenses |
For real estate firms, most property leases are classified as operating leases, which means they now appear on your balance sheet as both assets and liabilities.
Getting ASC 842 right requires a structured approach. Read the PDF below and follow the steps to ensure you’re compliant without missing critical details.
ASC 842 significantly changes your financial metrics. Understanding these impacts helps you communicate with lenders, investors, and stakeholders.
The Impact: These ratios increase because lease liabilities now appear on your balance sheet as debt.
Before ASC 842: A real estate firm with $100 million in assets and $50 million in equity had a debt-to-equity ratio of 1.0 (if $50 million in debt).
After ASC 842: If the same firm recognized $30 million in operating lease liabilities, the debt-to-equity ratio increases to 1.6 (now $80 million in total debt ÷ $50 million equity).
Why This Matters: Lenders and credit rating agencies use these ratios to assess financial risk. A higher ratio might affect your borrowing costs or credit availability.
The Impact: This ratio decreases because current lease liabilities increase the denominator.
Current Ratio = Current Assets ÷ Current Liabilities
When you add current portions of lease liabilities to current liabilities, your current ratio typically declines, potentially affecting assessments of your short-term financial health.
The Impact: EBITDA typically increases under ASC 842.
Under ASC 840, operating lease payments were simple rent expenses. Under ASC 842, they’re split into two components:
Since both are excluded from EBITDA, your EBITDA may increase compared to the old standard. This can actually benefit real estate firms with significant lease portfolios.
The Impact: ROA typically decreases.
ROA = Net Income ÷ Average Total Assets
Since ASC 842 adds ROU assets to your balance sheet, total assets increase. If net income remains relatively stable, ROA decreases.
Critical Point: If your loan agreements contain financial covenants based on leverage ratios or EBITDA, ASC 842 may trigger unintentional covenant breaches.
Proactive Steps:
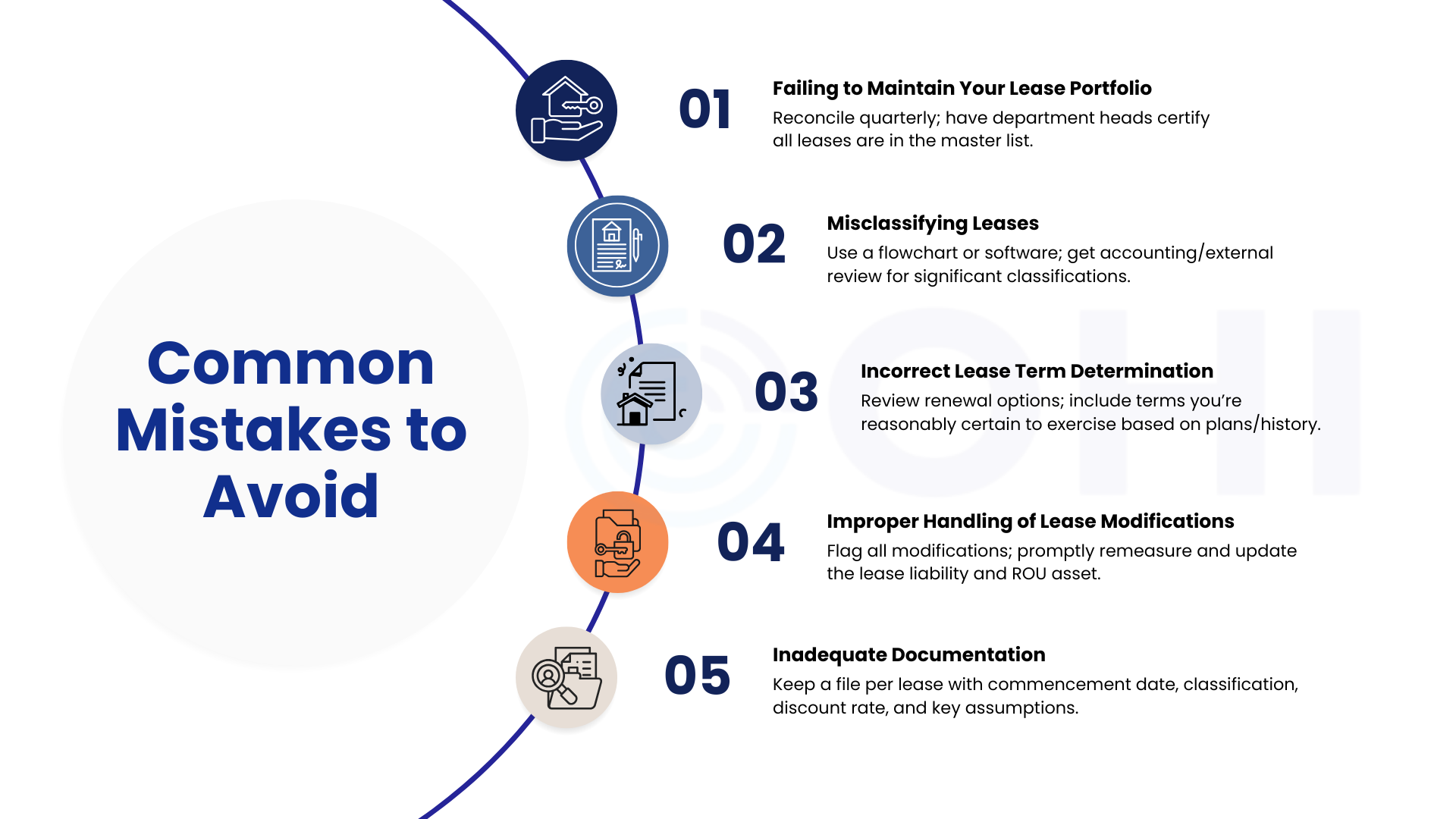
Real estate firms face unique compliance challenges. Below is the infographic showing the most common issues and how to address them.

Not every agreement is subject to full ASC 842 accounting. There are two important exemptions.
Definition: A lease with a term of 12 months or less, with no purchase option the lessee is reasonably certain to exercise.
Treatment: You can elect to recognize lease payments as an expense on a straight-line basis without recording an ROU asset or lease liability on the balance sheet.
Application: You make this election by class of underlying asset. You can choose to elect it for equipment leases but not for real estate leases, for example.
Real Estate Implication: Most real estate leases are longer than 12 months, so this exemption rarely applies to property. However, short-term parking agreements or temporary storage leases might qualify.
Definition: A lease of an asset with a fair value of $5,000 or less at lease commencement.
Treatment: You can elect to recognize lease payments as an expense without recording an ROU asset or lease liability.
Conditions: The asset must be able to benefit you on its own or combined with readily available resources. It cannot be highly dependent on or integrated with other assets.
Real Estate Implication: Low-value leases in a real estate portfolio might include leases of small equipment, office furniture, or similar items. However, most real estate space exceeds $5,000 in value, so this exemption rarely applies.
For many real estate firms, manual spreadsheet-based ASC 842 compliance is time-consuming and error-prone. Specialized software can simplify compliance significantly.
Automated Data Capture: Many tools use AI and optical character recognition (OCR) to extract data from lease contracts, reducing manual data entry.
Automated Calculations: The software calculates lease liabilities, ROU assets, depreciation, and interest automatically, reducing calculation errors.
Lease Modification Tracking: Software flags when leases are modified and automatically recalculates balances.
Audit Trails: Detailed records show every calculation, assumption, and change, making audits easier.
Centralized Lease Register: All lease data lives in one place, eliminating scattered spreadsheets.
Automated Reporting: Generates financial statement disclosures automatically.
While there are many options, popular choices include MRI Software, Nakisa Lease Administration, Visual Lease, and Trullion. Each offers different features, integrations, and pricing models. When evaluating software, consider your firm’s size, number of leases, and integration needs.
A small real estate firm with 10-20 leases might manage ASC 842 compliance with spreadsheets and some accounting support. A mid-sized firm with 50+ leases often finds that software pays for itself through reduced accounting labor and fewer errors.

Real estate firms face unique ASC 842 challenges compared to other industries. Here’s what you need to know.
If you own and lease property to tenants, ASC 842 affects how you account for your leases to tenants. As the lessor, you must determine whether each tenant lease is operating or sales-type, recognize revenue appropriately, and maintain detailed records of lease terms.
Key Point: Even if your business model is primarily leasing property to others, ASC 842 still applies to any leases your company enters into (such as leasing office space for management operations).
If you manage properties on behalf of others, your role in ASC 842 compliance involves:
If your real estate firm leases office, warehouse, or retail space, ASC 842 requires you to:
Real estate firms with properties across multiple locations face additional complexity:
Solution: Centralize data collection and implement consistent policies across all locations. Use software that can handle multiple entities, currencies, and jurisdictions.
ASC 842 requires extensive disclosures. Your financial statements must include:
Real Estate Requirement: The lease maturity analysis is particularly important. You must show the undiscounted future lease payments for your real estate leases separately from other lease payments.
If you’re newly compliant with ASC 842, you must provide the full annual disclosures in each quarterly report (10-Q) for the first year, in addition to your annual report (10-K).
Auditors pay close attention to ASC 842 compliance. Here’s what to prepare.
Auditors typically:
Whether you’re newly complying with ASC 842 or refining ongoing compliance, here’s a realistic timeline:
| Phase | Timeline | Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Planning | Months 1-2 | Educate team, assess impacts, select software (if needed) |
| Lease Identification | Months 2-4 | Create lease inventory, identify embedded leases, collect contracts |
| Data Collection | Months 3-5 | Gather lease terms, payment details, and discount rates |
| Analysis & Calculation | Months 4-6 | Classify leases, calculate liabilities, prepare ROU asset calculations |
| System Setup | Months 3-6 | Configure software, create accounts, set up processes |
| Recording & Adjustments | Months 5-7 | Record initial journal entries, make adjustments for items like rent abatements |
| Testing & Review | Months 6-8 | Internal testing, review with accounting team, prepare audit documentation |
| Audit & Finalization | Months 7-9 | Respond to audit requests, finalize disclosures, publish financial statements |
| Ongoing Compliance | Ongoing | Monitor new leases, track modifications, maintain register |

ASC 842 represents a significant change in how leases are accounted for and reported. For real estate firms, understanding and implementing this standard correctly is essential for accurate financial reporting, audit success, and effective communication with investors and lenders.
The framework outlined in this guide—identifying leases, gathering data, classifying correctly, calculating accurately, and maintaining ongoing compliance—removes the mystery from ASC 842. By following these steps and leveraging available technology and professional resources, real estate firms can achieve full compliance while managing complexity effectively.
The key is to start early, assemble the right team (including accounting, real estate, legal, and procurement professionals), document your judgments carefully, and maintain organized records. With these in place, ASC 842 compliance becomes a manageable part of your regular financial processes rather than an overwhelming project.
Remember: ASC 842 is here to stay. By addressing it proactively now, you position your real estate firm for long-term compliance success and demonstrate financial transparency to all stakeholders.
ASC 842 compliance doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Follow these principles:
Why should companies outsource ASC 842 lease accounting?
Outsourcing ASC 842 helps companies manage complex lease data, calculations, and disclosures without overloading internal teams. It reduces compliance risk, improves accuracy, and ensures timely reporting—especially for organizations with large or changing lease portfolios.
2) What ASC 842 tasks can be outsourced?
Companies commonly outsource:
3) Is outsourcing ASC 842 cost-effective?
Yes. Outsourcing is often more cost-effective than hiring and training in-house specialists, particularly for mid-sized companies or real estate portfolios with frequent lease changes.
4) Can outsourced teams work within our existing lease accounting software?
Yes. Experienced outsourcing providers work directly within your current lease accounting or ERP systems, eliminating the need for new tools or system changes.
5) How does outsourcing help with ongoing ASC 842 compliance?
Outsourcing ensures leases are updated for renewals, amendments, terminations, and remeasurements—helping maintain continuous compliance beyond initial ASC 842 implementation.
6) Is ASC 842 outsourcing suitable for real estate-heavy companies?
Absolutely. Companies with multiple properties, locations, or lease types benefit most from outsourcing due to the volume of data, recurring updates, and reporting complexity.
7) What information is required to outsource ASC 842 lease accounting?
Typically required inputs include lease agreements, amendments, payment schedules, and system access (if applicable). The outsourcing team handles abstraction, validation, and processingHow do companies maintain control when outsourcing lease accounting?
Control is maintained through defined workflows, review checkpoints, documented assumptions, and regular reporting—allowing internal teams to approve and oversee outputs.
8) Does outsourcing ASC 842 support audits?
Yes. Outsourced lease accounting teams prepare audit-ready schedules, supporting documentation, and reconciliations, making audits faster and smoother.
9) When is the right time to outsource ASC 842?
Companies often outsource:
Contact us for a customized NO OBLIGATION proposal for outsourcing your accounting activities.









